 How Is Blown Film Made?
How Is Blown Film Made?
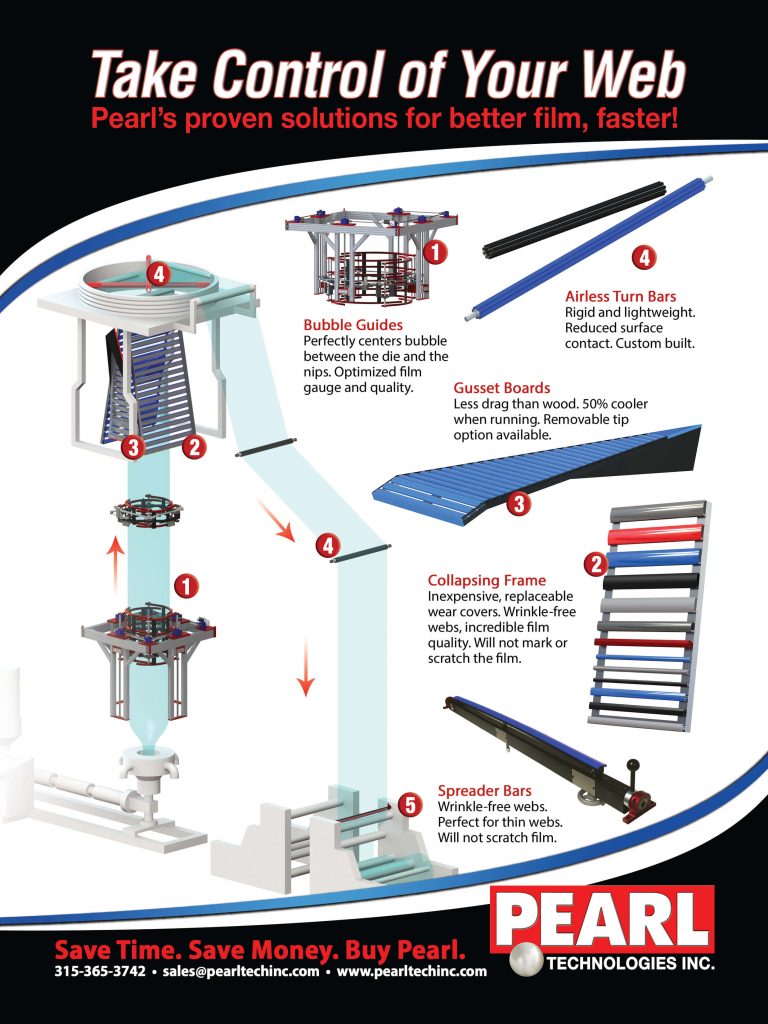
In the blown film process, resin is melted and then emerges from a circular die. This creates a thick layer of extruded film. Once the film comes out of the die, an air bubble is blown into the film to make it expand and reach the desired thickness.
The bubble cools as it is pulled upward by rollers. Eventually, the bubble collapses into a thin, flat tube of film and is wound up for storage. Once the bubble cools and collapses, it’s sent to the winding and slitting station for further processing and final finishing.
The ultimate gauge (thickness) of the material is determined by the original thickness and diameter of the extruded resin tube, as well as the total volume of the air bubble.
The Pros & Cons Of Blown Film
Wondering what the benefits of blown film may be for your company? Here is a look at a few pros and cons of blown film.
Blown Film Pros
- Enhanced puncture resistance
- Provides maximum toughness and durability
- Blown scrap has a high level of cling
- Produces less overall manufacturing scrap
- Stretches further than cast film
Blown Film Cons
- Reduced transparency & clarity
- Less effective cooling process
- Higher thickness variations
- Lower melt flow index
- Slower production rates
Blown film has its own unique pros and cons. But at Pearl Technologies, we specialize in blown film products that help maximize efficiency and product quality – and provide our customers with the highest possible quality in their production lines. Learn more about our extrusion solutions here.

